The Role of Foot Health in Preventing Falls and Injuries
Falls are a leading cause of injury-related hospitalization and mortality among older adults. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately one in four adults over the age of 65 falls each year, with 20% of these falls resulting in serious injuries such as fractures or head trauma (CDC, 2023). While fall prevention strategies often focus on strength training, environmental modifications, and medication adjustments, one critical yet frequently overlooked factor is foot health. Proper foot health plays a central role in maintaining balance, stability, and mobility. Misalignment, poor arch support, and improper footwear can increase the risk of falls, while interventions such as foot-strengthening exercises, orthotic support, and appropriate footwear selection can significantly reduce fall risk. This article explores the relationship between foot health and fall prevention, emphasizing how targeted foot care can improve balance and stability, particularly in seniors and individuals with mobility issues.
The Impact of Foot Health on Balance and Stability
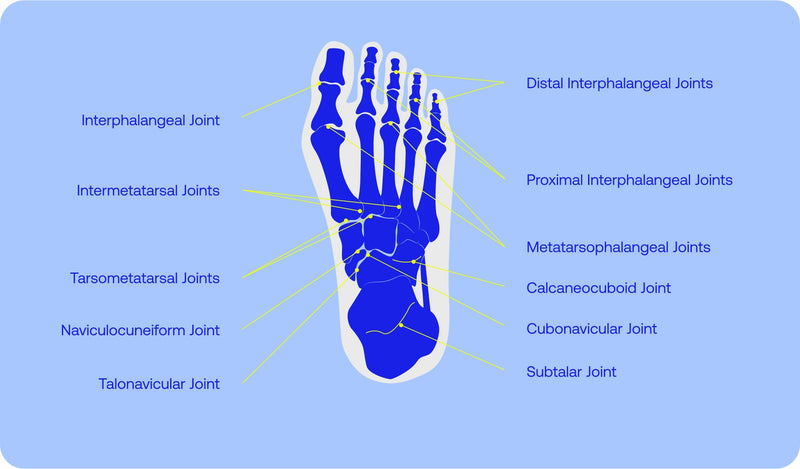
The human foot is a complex structure consisting of 26 bones, 33 joints, and more than 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments that work together to support body weight and facilitate movement (Menz et al., 2008). Proper foot alignment and function are essential for balance and gait stability. Even minor impairments in foot mechanics can disrupt postural control, leading to instability and increased fall risk.
Foot problems such as plantar fasciitis, bunions, hammer toes, arthritis, and peripheral neuropathy are common in older adults and are strongly correlated with balance deficits and an increased risk of falls (Spink et al., 2011). For example, peripheral neuropathy, which involves damage to the nerves in the feet, can reduce sensation and proprioception— the body's ability to sense its position in space—resulting in unsteady gait patterns and poor balance control (Richardson et al., 2004).
A study by Menz and Lord (1999) found that 87% of older adults had at least one foot problem, which was significantly associated with poor balance and an increased likelihood of falling. Common foot deformities and conditions such as flat feet, overpronation, and joint stiffness were linked to slower walking speeds, reduced step length, and impaired postural control—all of which increase the risk of falls (Menz et al., 2001). Therefore, maintaining optimal foot health through proper alignment, support, and strength is essential for enhancing stability and preventing falls.
Misalignment and Poor Arch Support: A Hidden Risk Factor
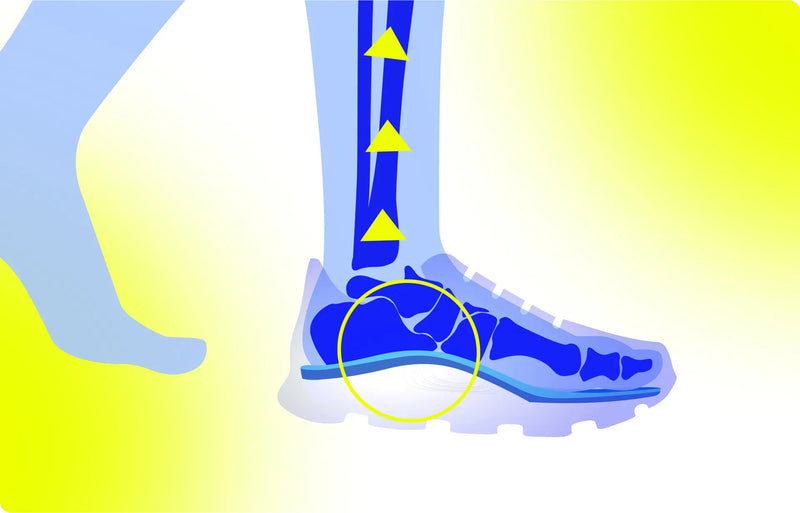
Foot misalignment and inadequate arch support are key contributors to fall risk. When the foot’s natural arch collapses or becomes misaligned, the body’s center of gravity shifts, leading to uneven weight distribution and poor balance control. Overpronation (excessive inward rolling of the foot) and supination (excessive outward rolling) can lead to muscle fatigue, joint strain, and gait instability.
Improper footwear can exacerbate these issues. Shoes that lack proper arch support, cushioning, or a secure fit can impair postural stability and increase fall risk (Menant et al., 2008). Footwear with thin soles, high heels, or excessive flexibility has been linked to poor balance and increased fall rates among older adults (Menant et al., 2008). A study by Sherrington et al. (2011) found that modifying footwear to include supportive, well-fitted shoes with non-slip soles reduced fall risk by 36% among community-dwelling seniors.
To counteract these problems, medical-grade insoles such as VALSOLE stable support insoles can improve foot alignment and provide enhanced arch support. These insoles are designed to redistribute pressure evenly across the foot, reduce overpronation, and stabilize gait patterns, which helps to improve balance and reduce the likelihood of falls (Hatton & Rome, 2019).
Enhancing Proprioception and Stability Through Foot Care
Proprioception—the body's ability to detect its position and movement—is essential for maintaining balance and stability. The feet contain a high concentration of sensory receptors that provide critical feedback to the brain regarding changes in surface texture, body positioning, and weight distribution (Richardson et al., 2004). When foot health is compromised due to misalignment, poor muscle tone, or nerve damage, proprioceptive feedback is diminished, leading to impaired balance and increased fall risk.
Medical-grade insoles can enhance proprioceptive feedback by providing consistent contact and support to the foot's pressure points. VALSOLE stable support insoles, for example, are designed to improve sensory input and foot positioning, which can enhance balance and stability during walking and standing.
Additionally, targeted foot exercises can improve proprioception and muscle strength. Exercises such as toe raises, heel-to-toe walking, and single-leg balancing help to activate the intrinsic muscles of the foot, improving joint stability and postural control (Menz et al., 2008). A study by Spink et al. (2011) demonstrated that a comprehensive foot care program, including strengthening exercises and orthotic support, reduced the incidence of falls by 36% among older adults with disabling foot pain.
Foot Exercises for Balance and Stability
Incorporating foot exercises into daily routines can strengthen the muscles that support the arch, improve joint mobility, and enhance proprioceptive feedback. Effective exercises include:
-
Toe curls: Strengthens the intrinsic muscles of the foot, improving grip and balance.
-
Heel raises: Activates the calf muscles and strengthens the arch, promoting better weight distribution.
-
Ankle circles: Improves joint mobility and flexibility.
-
Single-leg balance: Enhances postural control and foot strength.
Regular practice of these exercises has been shown to improve gait patterns and postural stability, thereby reducing fall risk (Menz et al., 2008). Healthcare providers should educate patients on the importance of foot strength and flexibility as part of a comprehensive fall prevention strategy.
Selecting the Right Footwear for Fall Prevention
Footwear selection is a critical aspect of fall prevention. Research indicates that shoes with a wide toe box, firm heel counter, and non-slip soles provide the greatest stability and support for older adults (Menant et al., 2008). Key features to look for in fall-prevention footwear include:
-
Arch support: Enhances weight distribution and alignment.
-
Firm heel counter: Provides rearfoot stability and prevents heel slippage.
-
Non-slip soles: Improves traction and reduces slipping risk.
-
Adjustable fit: Ensures comfort and proper alignment.
VALSOLE stable support insoles can be incorporated into appropriate footwear to further enhance foot stability and alignment. The combination of supportive footwear and insoles improves overall postural control, reduces muscle fatigue, and minimizes fall risk (Hatton & Rome, 2019).
Integrating Foot Care into Fall Prevention Programs
Comprehensive fall prevention programs should include regular foot health assessments, targeted exercises, and appropriate footwear recommendations. Healthcare providers can play a pivotal role in identifying foot problems that contribute to instability and prescribing corrective measures such as orthotic support and strengthening exercises.
Programs that include podiatric interventions have been shown to reduce fall rates significantly. A study by Spink et al. (2011) found that a multifaceted podiatric intervention—including foot orthoses, shoe modifications, and exercise—reduced falls by 36% among older adults with disabling foot pain. Such evidence underscores the importance of foot health as a critical component of fall prevention strategies.
Foot health is a foundational element of fall prevention. Misalignment, poor arch support, and inadequate footwear are significant but often overlooked contributors to falls among older adults. Addressing these issues through targeted exercises, medical-grade insoles like VALSOLE stable support insoles, and proper footwear selection can significantly enhance balance and stability. Healthcare professionals should integrate foot health assessments and interventions into comprehensive fall prevention programs to improve overall patient outcomes and reduce fall-related injuries.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2023). Older adult falls: Data and statistics. https://www.cdc.gov
Hatton, A. L., & Rome, K. (2019). Falls, footwear, and podiatric interventions in older adults. Clinics in Geriatric Medicine, 35(2), 161-171.
Menant, J. C., Steele, J. R., Menz, H. B., Munro, B. J., & Lord, S. R. (2008). Effects of footwear features on balance and stepping in older people. Gerontology, 54(1), 18-23.
Menz, H. B., & Lord, S. R. (1999). Foot problems, functional impairment, and falls in older people. Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association, 89(9), 458-467.
Spink, M. J., Menz, H. B., Fotoohabadi, M. R., Wee, E., Landorf, K. B., & Hill, K. D. (2011). Effectiveness of a podiatry intervention to prevent falls in older people. BMJ, 342, d3411.